前言
在Android Q上,google为了加快应用的启动速度。在zygote fork阶段,采用了线程池的方式,来加快fork的过程。
首先,如果让我们自己做,肯定会选择java的线程池模型,先创建N个进程,当需要fork的时候,取出来一个来bindapplication,同时进行补充进程池。
但是google的做法并不是这样,google的思路是:同时fork N个进程,监听同一个socket fd,当收到消息的时候,只有一个进程会被唤醒,来处理这个消息。google利用了这样的一个机制,来进行进程池的处理。
流程
首先先来一个流程图来概览一下,本文基于Android Q。
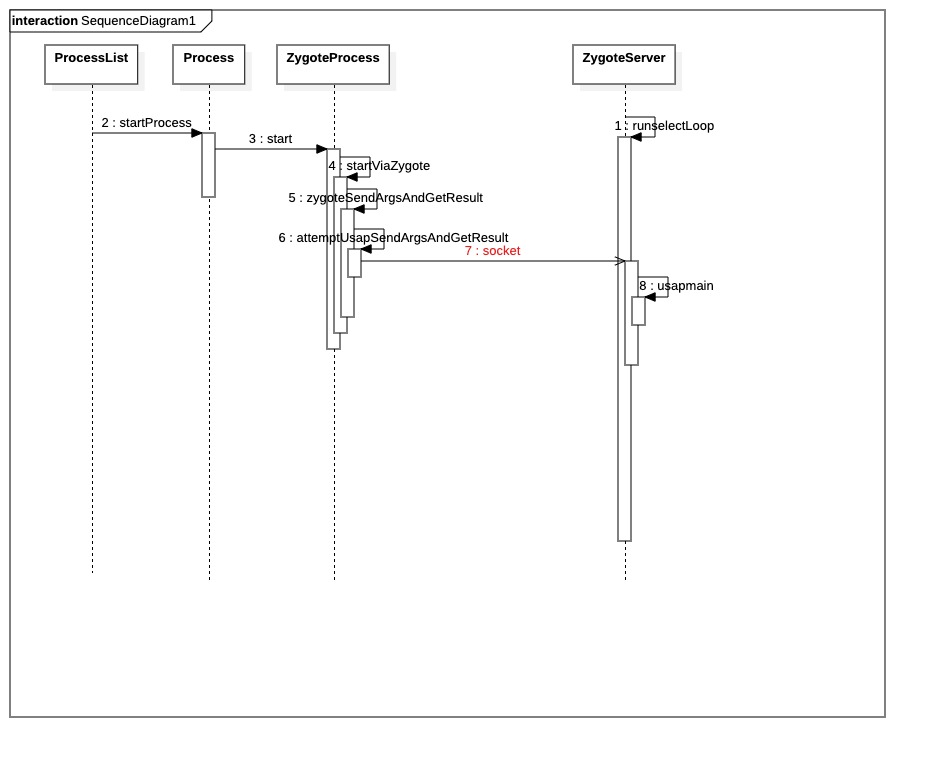 简述一下就是:
简述一下就是:
- system_server 向 usap_pool_primary的socket发送信息。
- zygote fork了N个进程监听 usap_pool_primary的socket。
- 当usap_pool_primary收到消息后,唤醒其中一个来处理对应的操作。
system_server中的流程
我们都知道,Android中的进程启动其实都是activity或者是service,或者是contentprovider,入口都是在ProcessList中
// frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ProcessList.java
private Process.ProcessStartResult startProcess(HostingRecord hostingRecord, String entryPoint,
ProcessRecord app, int uid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int zygotePolicyFlags,
int mountExternal, String seInfo, String requiredAbi, String instructionSet,
String invokeWith, long startTime) {
...
final Process.ProcessStartResult startResult;
if (hostingRecord.usesWebviewZygote()) { // 如果是使用的webview,那么就通过这个方式
startResult = startWebView(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName, app.mDisabledCompatChanges,
new String[]{PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
} else if (hostingRecord.usesAppZygote()) { // 如果会使用 app_zygote的流程
final AppZygote appZygote = createAppZygoteForProcessIfNeeded(app);
startResult = appZygote.getProcess().start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName,
/*zygotePolicyFlags=*/ ZYGOTE_POLICY_FLAG_EMPTY, isTopApp,
app.mDisabledCompatChanges,
new String[]{PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
} else { // 我们正常的应用启动,服务启动流程
startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, app.info.packageName, zygotePolicyFlags,
isTopApp, app.mDisabledCompatChanges,
new String[]{PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
}
checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: returned from zygote!");
return startResult;
}
在ProcessList中进行start操作的区分,区分webview和app_zygote(这也是一个历史的问题,我们可以后面讲到)。然后就是我们最熟悉的activity的启动过程。
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Process.java
public static ProcessStartResult start(@NonNull final String processClass,
@Nullable final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, @Nullable int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags,
int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
@Nullable String seInfo,
@NonNull String abi,
@Nullable String instructionSet,
@Nullable String appDataDir,
@Nullable String invokeWith,
@Nullable String packageName,
int zygotePolicyFlags,
boolean isTopApp,
@Nullable long[] disabledCompatChanges,
@Nullable String[] zygoteArgs) {
return ZYGOTE_PROCESS.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, packageName,
zygotePolicyFlags, isTopApp, disabledCompatChanges, zygoteArgs);
}
注意此处了zygotePolicyFlags,这个地方就是是否要使用usappool的地方。默认在q上都是true。
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
public final Process.ProcessStartResult start(@NonNull final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, @Nullable int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
@Nullable String seInfo,
@NonNull String abi,
@Nullable String instructionSet,
@Nullable String appDataDir,
@Nullable String invokeWith,
@Nullable String packageName,
int zygotePolicyFlags,
boolean isTopApp,
@Nullable long[] disabledCompatChanges,
@Nullable String[] zygoteArgs) {
// TODO (chriswailes): Is there a better place to check this value?
if (fetchUsapPoolEnabledPropWithMinInterval()) { // 如果是支持线程池的话,那么需要通知zygote去创建线程
informZygotesOfUsapPoolStatus(); // 通知zygote去创建线程
}
try {
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, /*startChildZygote=*/ false,
packageName, zygotePolicyFlags, isTopApp, disabledCompatChanges, zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
throw new RuntimeException(
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
}
}
此处需要主要那个TODO, 如备注所讲,如果zygote能够支持线程池的话,需要通知zygote去创建线程池。那么问题就来了,那岂不是每次启动都需要去检查一次,那岂不是很耗费资源?所以确实是这样,如果是我们去设计,这块肯定会是需要做一个监听或者回调的,可以直接check这个值,而不是每次启动都需要去查询。
// frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
private Process.ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(@NonNull final String processClass,
@Nullable final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
.....
{
synchronized(mLock) {
// The USAP pool can not be used if the application will not use the systems graphics
// driver. If that driver is requested use the Zygote application start path.
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi),
zygotePolicyFlags,
argsForZygote);
}
}
private Process.ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, int zygotePolicyFlags, @NonNull ArrayList<String> args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
...
String msgStr = args.size() + "\n" + String.join("\n", args) + "\n";
if (shouldAttemptUsapLaunch(zygotePolicyFlags, args)) {
try {// 采用 usap的方式启动应用
return attemptUsapSendArgsAndGetResult(zygoteState, msgStr);
} catch (IOException ex) {
// If there was an IOException using the USAP pool we will log the error and
// attempt to start the process through the Zygote.
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "IO Exception while communicating with USAP pool - "
+ ex.getMessage());
}
}
return attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(zygoteState, msgStr);
}
private Process.ProcessStartResult attemptUsapSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, String msgStr)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx, IOException {
try (LocalSocket usapSessionSocket = zygoteState.getUsapSessionSocket()) {
final BufferedWriter usapWriter =
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(usapSessionSocket.getOutputStream()),
Zygote.SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE);
final DataInputStream usapReader =
new DataInputStream(usapSessionSocket.getInputStream());
usapWriter.write(msgStr); // 向usap_pool的socket中发送命令
usapWriter.flush();
Process.ProcessStartResult result = new Process.ProcessStartResult();
result.pid = usapReader.readInt();
// USAPs can't be used to spawn processes that need wrappers.
result.usingWrapper = false;
if (result.pid >= 0) {
return result;
} else {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("USAP specialization failed");
}
}
}
好的,到了这里,我们就把system_server这边的流程梳理完成了。 过程就是:
- processList在启动activity的时候,使用了独特的flag
- 启动之前检查一下,zygote是否已经完成了线程池的初始化
- 发送参数给usap_pool_primary的socket
zygote逻辑
zygote的逻辑简述:
- fork出对应的进程,并且进行标记
- 维护线程数量
应用启动流程就不再赘述,此处摘录一下zygoteinit部分代码
// frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;
// runslectloop中包含了fork操作,子进程会返回对应的caller的runnable,而zygote并不会返回,这样就进行了区分
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.
if (caller != null) {
caller.run();
}
}
zygote fork出来的子进程在返回对应的runnable,然后对runnable进行初始化的操作,这样app_process就完成了对应的初始化。下面我们详细的来看一下runselectloop
// frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteServer.java
Runnable runSelectLoop(String abiList) {
while (true) {
fetchUsapPoolPolicyPropsWithMinInterval(); // 获取usap pool的属性
if (mUsapPoolEnabled) {
usapPipeFDs = Zygote.getUsapPipeFDs();
pollFDs = new StructPollfd[socketFDs.size() + 1 + usapPipeFDs.length];
} else {
pollFDs = new StructPollfd[socketFDs.size()];
}
int pollIndex = 0;
for (FileDescriptor socketFD : socketFDs) {
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = socketFD;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
}
final int usapPoolEventFDIndex = pollIndex;
if (mUsapPoolEnabled) { // 将需要监听的fd整合在一起
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = mUsapPoolEventFD;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
// The usapPipeFDs array will always be filled in if the USAP Pool is enabled.
assert usapPipeFDs != null;
for (int usapPipeFD : usapPipeFDs) {
FileDescriptor managedFd = new FileDescriptor();
managedFd.setInt$(usapPipeFD);
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = managedFd;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
}
}
int pollReturnValue;
try {
pollReturnValue = Os.poll(pollFDs, pollTimeoutMs); // 进入监听
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
if (pollReturnValue == 0) {
// The poll timeout has been exceeded. This only occurs when we have finished the
// USAP pool refill delay period.
mUsapPoolRefillTriggerTimestamp = INVALID_TIMESTAMP;
mUsapPoolRefillAction = UsapPoolRefillAction.DELAYED;
} else {
boolean usapPoolFDRead = false;
while (--pollIndex >= 0) { // 监听的fd被触发
if ((pollFDs[pollIndex].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (pollIndex == 0) {
// Zygote server socket
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
socketFDs.add(newPeer.getFileDescriptor());
} else if (pollIndex < usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
// 未使用usap pool的流程
} else {
long messagePayload;
try {
byte[] buffer = new byte[Zygote.USAP_MANAGEMENT_MESSAGE_BYTES];
int readBytes =
Os.read(pollFDs[pollIndex].fd, buffer, 0, buffer.length);
if (readBytes == Zygote.USAP_MANAGEMENT_MESSAGE_BYTES) {
DataInputStream inputStream =
new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(buffer));
messagePayload = inputStream.readLong();
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Incomplete read from USAP management FD of size "
+ readBytes);
continue;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (pollIndex == usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read from USAP pool event FD: "
+ ex.getMessage());
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read from USAP reporting pipe: "
+ ex.getMessage());
}
continue;
}
if (pollIndex > usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
Zygote.removeUsapTableEntry((int) messagePayload);
}
usapPoolFDRead = true; // 说明我们使用了usap pool,后面就需要对usap pool进行维护
}
}
// 对usap pool进行维护,包含了 fd的处理,如果池子数量不多还需要进行补充
if (mUsapPoolRefillAction != UsapPoolRefillAction.NONE) {
int[] sessionSocketRawFDs =
socketFDs.subList(1, socketFDs.size())
.stream()
.mapToInt(FileDescriptor::getInt$)
.toArray();
final Runnable command =
fillUsapPool(sessionSocketRawFDs, isPriorityRefill);
if (command != null) { // 子进程返回给zygoteinit,执行run方法,zygote进程继续循环。
return command;
} else if (isPriorityRefill) {
// Schedule a delayed refill to finish refilling the pool.
mUsapPoolRefillTriggerTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
} }
}
现在我们理所当然的按之前的思路去想:正常的app启动流程:收到消息后,在processOnecommand中去进行fork,然后进行 pid,gid的赋予也就是forkAndSpecialize。但是在这里一看,不对啊,这个时候收到的已经是pid,gid赋予后的进程了。那么究竟是什么时候进行的这个过程呢?
我们只能慢慢的往后看,对进程池进行维护的过程:
// frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteServer.java
Runnable fillUsapPool(int[] sessionSocketRawFDs, boolean isPriorityRefill) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Zygote:FillUsapPool");
// Disable some VM functionality and reset some system values
// before forking.
ZygoteHooks.preFork();
while (--numUsapsToSpawn >= 0) {
// fork对应的子进程
Runnable caller =
Zygote.forkUsap(mUsapPoolSocket, sessionSocketRawFDs, isPriorityRefill);
if (caller != null) {
return caller;
}
}
ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon();
resetUsapRefillState();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
return null;
}
这里也就是创建了一个子进程
// frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygote.java
static Runnable forkUsap(LocalServerSocket usapPoolSocket,
int[] sessionSocketRawFDs,
boolean isPriorityFork) {
FileDescriptor[] pipeFDs = null;
try {
pipeFDs = Os.pipe2(O_CLOEXEC);
} catch (ErrnoException errnoEx) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to create USAP pipe.", errnoEx);
}
// 此处fork出了pid
int pid =
nativeForkUsap(pipeFDs[0].getInt$(), pipeFDs[1].getInt$(),
sessionSocketRawFDs, isPriorityFork);
// 如果是子进程
if (pid == 0) {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(pipeFDs[0]);
return usapMain(usapPoolSocket, pipeFDs[1]);
} else { // zygote进程直接返回null
// The read-end of the pipe will be closed by the native code.
// See removeUsapTableEntry();
IoUtils.closeQuietly(pipeFDs[1]);
return null;
}
}
注意关注注释的位置,在进程池进行维护的时候,就已经通过底层的forkcommon,创建出了对应的子进程,那我们看看子进程做了哪些操作
// frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygote.java
private static Runnable usapMain(LocalServerSocket usapPoolSocket,
FileDescriptor writePipe) {
// 关键操作 warning!!!!
sessionSocket = usapPoolSocket.accept();
// 进行uid,gid的赋值操作
specializeAppProcess(args.mUid, args.mGid, args.mGids,
args.mRuntimeFlags, rlimits, args.mMountExternal,
args.mSeInfo, args.mNiceName, args.mStartChildZygote,
args.mInstructionSet, args.mAppDataDir, args.mIsTopApp);
}
乍一看,我去,这刚fork出来的空进程,怎么就进行赋值了呢,这些数据是哪儿来的?仔细一看关键的节点,这些args也都是通过socket读取到的。所以此处的accept是一个阻塞操作。这里也涉及到socket的一个惊群效应,感兴趣的可以自行搜索一下。
总结
zygote使用进程池的思路完全和之前zygote的思路不同了。
之前zygote的思路像大总管,你们负责把参数发给我,然后我再fork,赋值uid,gid等,这样我的儿子就可以变成app_process了。
而现在的思路则是:我立刻分身成N个我自己,我和分身完全一样,你们可以直接和我的分身进行通信,得到通信的分身就可以直接转化成app_process,而我只用来负责创建分身和维护分身。