QUESTION:
There are n items each belonging to zero or one of m groups where group[i] is the group that the i-th item belongs to and it’s equal to -1 if the i-th item belongs to no group. The items and the groups are zero indexed. A group can have no item belonging to it.
Return a sorted list of the items such that:
- The items that belong to the same group are next to each other in the sorted list.
- There are some relations between these items where beforeItems[i] is a list containing all the items that should come before the i-th item in the sorted array (to the left of the i-th item). Return any solution if there is more than one solution and return an empty list if there is no solution.
Example 1:
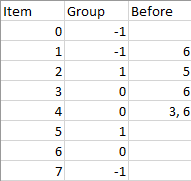
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3,6],[],[],[]]
Output: [6,3,4,1,5,2,0,7]
Example 2:
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3],[],[4],[]]
Output: []
Explanation: This is the same as example 1 except that 4 needs to be before 6 in the sorted list.
Constraints:
1 <= m <= n <= 3*10^4
group.length == beforeItems.length == n
-1 <= group[i] <= m-1
0 <= beforeItems[i].length <= n-1
0 <= beforeItems[i][j] <= n-1
i != beforeItems[i][j]
beforeItems[i] does not contain duplicates elements.
EXPLANATION:
终于来到了hard的题目,这道题目经过题意就可以看到也还是采用拓扑排序。但是此处有个问题:相同group的必须放在一起。那这我们就可以知道:不会出现交叉group出现的情况。那么就是必然是group进行排序的。此时,我们就可以知道:我们需要进行两步排序,首先对group进行排序,再对group中的每个item进行排序。
思路:
- 首先对item进行拓扑排序
- 对group进行拓扑排序
- 将item排序的填充到group中,这样group中的item就是已经排过序的
- 再对group按拓扑排序的顺序摆在一起
SOLUTION:
class Solution {
public int[] sortItems(int n, int m, int[] group, List<List<Integer>> beforeItems) {
// 计算item之间的拓扑
int[] inDgree = new int[n];
ArrayList<Integer>[] beforeGraph = new ArrayList[n];
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) beforeGraph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0;i<beforeItems.size();i++){
for(int child : beforeItems.get(i)){
inDgree[i]++;
beforeGraph[child].add(i);
}
}
// 将group为-1的设置为单独的group
int[] groupIndex = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;i<group.length;i++) {
if(group[i] == -1) group[i] = m++;
groupIndex[i] = group[i];
}
// 计算group之间的拓扑
int[] groupDgree = new int[m];
ArrayList<Integer>[] groupGraph = new ArrayList[m];
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++) groupGraph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0;i<group.length;i++){
int toGroup = group[i];
for(int child: beforeItems.get(i)){
int fromGroup = group[child];
if(fromGroup != toGroup){
groupGraph[fromGroup].add(toGroup);
groupDgree[toGroup]++;
}
}
}
// 对group和item进行拓扑排序
List<Integer> groupResult = topoHelper(groupDgree,groupGraph);
List<Integer> itemResult = topoHelper(inDgree,beforeGraph);
// 如果有环,则直接退出
if(groupResult.size()==0 || itemResult.size()==0) return new int[0];
// 整理每个group的排序结果
ArrayList<Integer>[] sortedGroups = new ArrayList[m];
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++) sortedGroups[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i : itemResult)
sortedGroups[group[i]].add(i);
// 将排序结果按group排完的顺序填充
int[] result = new int[n];
int index =0;
for(Integer grp: groupResult) {
for (Integer i : sortedGroups[grp])
result[index++] = i;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
return result;
}
public static List<Integer> topoHelper(int[] dgree,ArrayList<Integer>[] graph){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
for(int i = 0;i<dgree.length;i++) if(dgree[i]==0) queue.add(i);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int node = queue.poll();
list.add(node);
for(int child : graph[node]){
dgree[child]--;
if(dgree[child]==0) queue.add(child);
}
}
return list.size()==graph.length ? list: new ArrayList<>();
}
}