QUESTION:
Given a binary tree with the following rules:
root.val == 0 If treeNode.val == x and treeNode.left != null, then treeNode.left.val == 2 * x + 1 If treeNode.val == x and treeNode.right != null, then treeNode.right.val == 2 * x + 2 Now the binary tree is contaminated, which means all treeNode.val have been changed to -1.
You need to first recover the binary tree and then implement the FindElements class:
FindElements(TreeNode* root) Initializes the object with a contamined binary tree, you need to recover it first. bool find(int target) Return if the target value exists in the recovered binary tree.
Example 1:
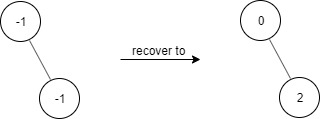
Input [“FindElements”,”find”,”find”] [[[-1,null,-1]],[1],[2]] Output [null,false,true] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1]); findElements.find(1); // return False findElements.find(2); // return True Example 2:
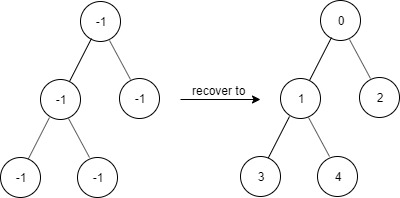
Input [“FindElements”,”find”,”find”,”find”] [[[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]],[1],[3],[5]] Output [null,true,true,false] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]); findElements.find(1); // return True findElements.find(3); // return True findElements.find(5); // return False Example 3:
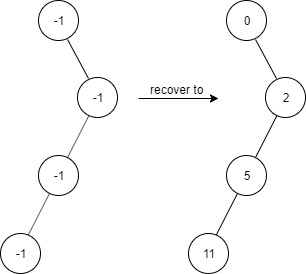
Input [“FindElements”,”find”,”find”,”find”,”find”] [[[-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]],[2],[3],[4],[5]] Output [null,true,false,false,true] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]); findElements.find(2); // return True findElements.find(3); // return False findElements.find(4); // return False findElements.find(5); // return True
Constraints:
TreeNode.val == -1 The height of the binary tree is less than or equal to 20 The total number of nodes is between [1, 10^4] Total calls of find() is between [1, 10^4] 0 <= target <= 10^6
EXPLANATION:
其实这道题目看起来是一个中等的题目,但是其实是两个easy的题目加起来的。一个是将被污染的二叉树进行恢复,恢复完成后进行查找。而这两步其实都是考的二叉树的遍历。无论你使用前序,中序,后续遍历其实都可以。
第一步:将污染的二叉树进行恢复。那么肯定是采用递归的方式,恢复的话需要知道parent的值,同时需要知道自己是在左树上还是在右树上,那既然需要知道这些信息,那么我们就将这些信息传递过去。递归的时候将每次的root.val和是否是左树进行传递。递归中进行计算当前root的值,同时再向下传递,递归结束就可以。
第二步:二叉树查找就更不用说了,前中后序随便选择一个,查看左右子树是否找到,进行或运算,只要其中一个找到了就是可以的。
SOLUTION:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class FindElements {
TreeNode root;
public FindElements(TreeNode root) {
this.root = root;
if (root != null) root.val = 0;
if (root.left != null)
FindElementsHelper(root.left, 0, true);
if (root.right != null)
FindElementsHelper(root.right, 0, false);
}
private void FindElementsHelper(TreeNode root,int value,boolean left){
if(left) root.val = 2*value+1;
else root.val = 2*value+2;
if (root.left != null)
FindElementsHelper(root.left, root.val, true);
if (root.right != null)
FindElementsHelper(root.right, root.val, false);
}
public boolean find(int target) {
return findHelper(target,root);
}
public boolean findHelper(int target,TreeNode node){
if(node.val == target) return true;
boolean left= false;
boolean right = false;
if(node.left!=null) left = findHelper(target,node.left);
if(node.right!=null) right = findHelper(target,node.right);
return left|right;
}
}
/**
* Your FindElements object will be instantiated and called as such:
* FindElements obj = new FindElements(root);
* boolean param_1 = obj.find(target);
*/