QUESTION:
Given two binary trees original and cloned and given a reference to a node target in the original tree.
The cloned tree is a copy of the original tree.
Return a reference to the same node in the cloned tree.
Note that you are not allowed to change any of the two trees or the target node and the answer must be a reference to a node in the cloned tree.
Follow up: Solve the problem if repeated values on the tree are allowed.
Example 1:
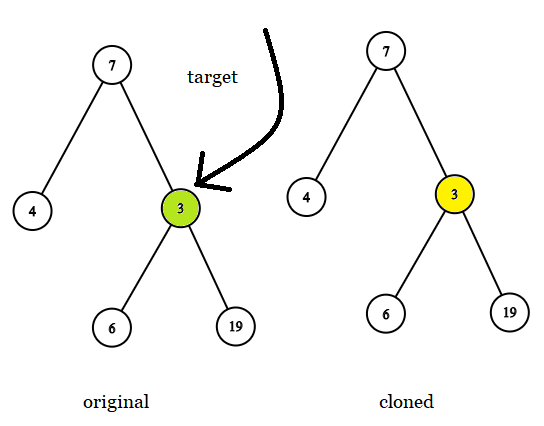
Input: tree = [7,4,3,null,null,6,19], target = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: In all examples the original and cloned trees are shown. The target node is a green node from the original tree. The answer is the yellow node from the cloned tree.
Example 2:
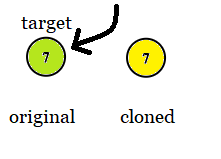
Input: tree = [7], target = 7
Output: 7
Example 3:
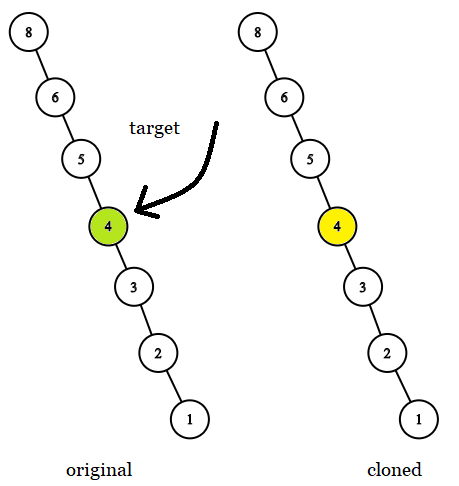
Input: tree = [8,null,6,null,5,null,4,null,3,null,2,null,1], target = 4
Output: 4
Example 4:
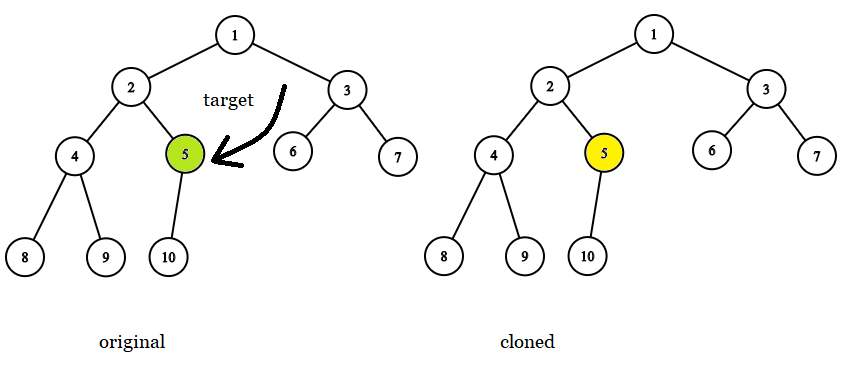
Input: tree = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], target = 5
Output: 5
Example 5:
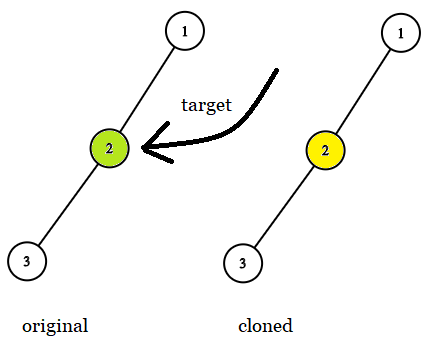
Input: tree = [1,2,null,3], target = 2
Output: 2
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 10^4].
The values of the nodes of the tree are unique.
target node is a node from the original tree and is not null.
EXPLANATION:
这道题目也很简单,其实就是一个二叉树的遍历,不论是前序,中序,还是后续其实都是可以的. 就不多说了. 关键是我看了最快的ac解. 他用了一个取巧的方式,直接用clone.val和target.val进行对比,来进行判断. 那这样题目的original和target的比较的意义就不存在了. 所以不可取.
SOLUTION:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode result;
public final TreeNode getTargetCopy(final TreeNode original, final TreeNode cloned, final TreeNode target) {
getTargetCopyHelper(original,cloned,target);
return result;
}
public void getTargetCopyHelper(TreeNode original, TreeNode cloned, TreeNode target) {
if (original == target) result = cloned;
if (original.left != null) getTargetCopy(original.left, cloned.left, target);
if (original.right != null) getTargetCopy(original.right, cloned.right, target);
}
}