QUESTION:
Given the root of a binary tree with N nodes, each node in the tree has node.val coins, and there are N coins total.
In one move, we may choose two adjacent nodes and move one coin from one node to another. (The move may be from parent to child, or from child to parent.)
Return the number of moves required to make every node have exactly one coin.
Example 1:
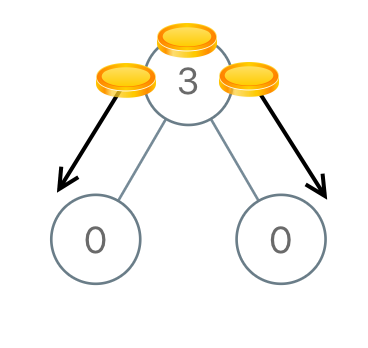
Input: [3,0,0] Output: 2 Explanation: From the root of the tree, we move one coin to its left child, and one coin to its right child. Example 2:
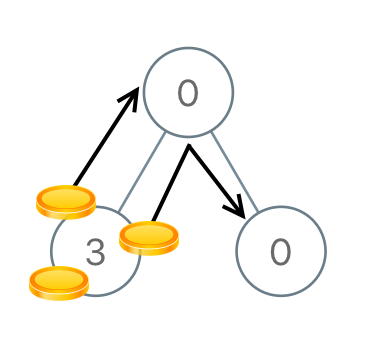
Input: [0,3,0] Output: 3 Explanation: From the left child of the root, we move two coins to the root [taking two moves]. Then, we move one coin from the root of the tree to the right child. Example 3:
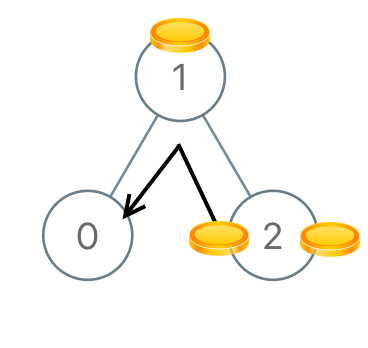
Input: [1,0,2] Output: 2 Example 4:
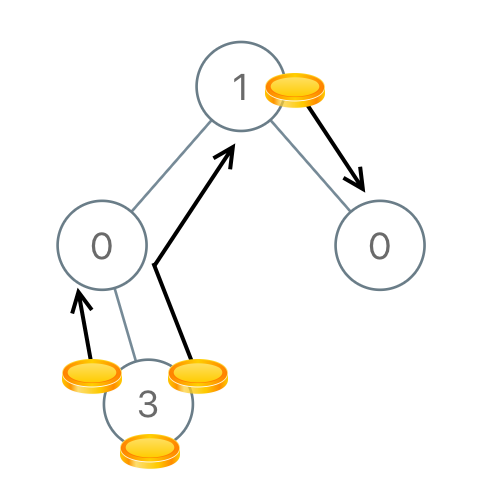
Input: [1,0,0,null,3] Output: 4
Note:
1<= N <= 100 0 <= node.val <= N
EXPLANATION:
我们可以知道是有n个节点,并且正好也有n个硬币。这是一个很关键的条件。有了这个条件,我们就可以确定,在最后根节点的时候,能保证左右两边coins+root.val就是n的节点数。那么这样思路就可以出来了。从最小的树开始,采用先序遍历的方式,来获取到每一个子树的需要的值。最后两边加在一起就是需要的步数了。
怎么将coin的个数和步数连接在一起呢?从两个最简单的例子开始:
- 300这个例子:左边节点需要1个,右边节点需要一个,所以就是需要2个,又因为3是根节点,所以确定了就是需要2步。
- 030这个例子:首先3这个节点本身需要1个,需要将另外2个推出去,因为不管这两个会推到哪里,其实都是需要2步,同时因为这个子树已经完成平衡,可以确定不需要再将新的coin推进来,所以这两个就是需要推出去的coin,也就是需要的步数,推给了自己的parent。 重复这个过程直到根节点。
SOLUTION:
class Solution { public int distributeCoinsStep = 0; public int distributeCoins(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return 0; distributeCoinsHelper(root); return distributeCoinsStep; } public int distributeCoinsHelper(TreeNode root){ int left = 0,right = 0; if(root.left!=null) left = distributeCoinsHelper(root.left); if(root.right!=null) right = distributeCoinsHelper(root.right); distributeCoinsStep += Math.abs(left) + Math.abs(right); return root.val+left+right-1; } }