QUESTION:
Given two lists of closed intervals, each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
(Formally, a closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b. The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that is either empty, or can be represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].)
Example 1:
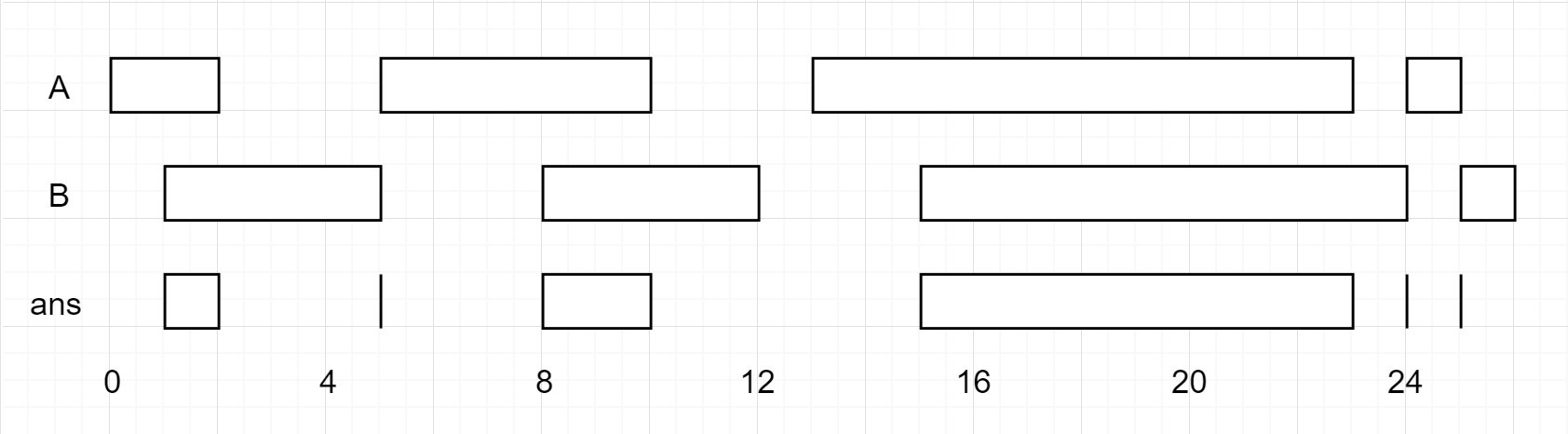
Input: A = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], B = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]] Reminder: The inputs and the desired output are lists of Interval objects, and not arrays or lists.
Note:
0 <= A.length < 1000 0 <= B.length < 1000 0 <= A[i].start, A[i].end, B[i].start, B[i].end < 10^9 NOTE: input types have been changed on April 15, 2019. Please reset to default code definition to get new method signature.
EXPLANATION:
这道题目的关键是如果你知道归并排序的话,那么就会知道这道题目的解题思路。因为题意已经很清楚的告诉你了,两个数组都是排序的,那么就是将他们合并成一个数组,和归并排序几乎相同,不同的是在合并的时候需要进行的操作。
那么先从A,B都是一个区间的情况下来进行合并,再推广到更多的数组。
- 首先确定相交的最小值: 那肯定就是low = MAX(A[0],B[0])
- 再确定相交的最大值: 那就是high = MIN(A[1],B[1])
- 如果low > high 就说明两者没有交集。否则就可以将结果保存到结果的list中
- 那么就需要确定high是A的终点还是B的,如果是A的就说明A区间已经用完,需要换到下一个
- 一直循环直到其中有一个数组结束为止
SOLUTION:
class Solution { public int[][] intervalIntersection(int[][] A, int[][] B) { ArrayList<int[]> result = new ArrayList<>(); int indexa = 0; int indexb = 0; while (indexa<A.length && indexb<B.length){ int[] tmpa = A[indexa]; int[] tmpb = B[indexb]; int low = Math.max(tmpa[0],tmpb[0]); int high = Math.min(tmpa[1],tmpb[1]); if(low<=high){ int[] tmp = new int[2]; tmp[0] = low; tmp[1] = high; result.add(tmp); } if(high == tmpa[1]) indexa++; if(high == tmpb[1]) indexb++; } int[][] arr = new int[result.size()][2]; for(int i = 0;i<result.size();i++) arr[i] = result.get(i); return arr; } }