前言
我们总是说ArrayMap是内存运用更高效的数据结构。那么究竟为什么,或者是什么样的操作来使内存优化呢。首先我们先说结论吧:ArrayMap其实依靠复用本身已经创建的mHashes和mArrays数组来进行内存的节省,这样就可以节省出创建和销毁对应数组的内存波动。
1.ArrayMap是如何解决hash碰撞的?
2.ArrayMap的内存节省究竟是如何做的?
ArrayMap是如何解决hash碰撞的?
public final class ArrayMap<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
int[] mHashes;
Object[] mArray;
}
所以这里盗用一下gityuan的图
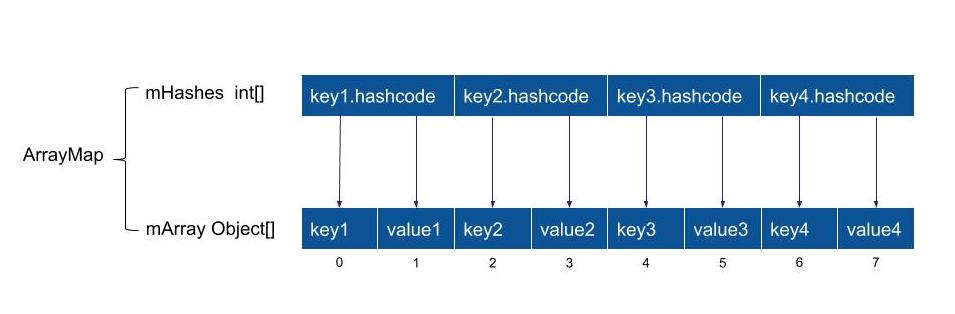 所以我们可以看到,mHashes里面保存了所有的hashcode,而mArray里面保存了对应的key,和value。
所以我们可以看到,mHashes里面保存了所有的hashcode,而mArray里面保存了对应的key,和value。
那么是如何解决hash碰撞呢?我们就需要从入口的put方法开始。
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
final int osize = mSize;
final int hash;
int index;
if (key == null) {
hash = 0;
index = indexOfNull();
} else { // 此处的默认为false
hash = mIdentityHashCode ? System.identityHashCode(key) : key.hashCode();
index = indexOf(key, hash);
}
if (index >= 0) {
index = (index<<1) + 1;
final V old = (V)mArray[index];
mArray[index] = value;
return old;
}
。。。。
所以我们是拿到的对应的key的hash值。那就需要看indexOf方法了。
int indexOf(Object key, int hash) {
final int N = mSize;
// 没有数据的情况,直接放在第一位
if (N == 0) {
return ~0;
}
// 二分查找位置
int index = binarySearchHashes(mHashes, N, hash);
// 没找到位置就直接返回
if (index < 0) {
return index;
}
// 找到了我们就需要看看是否就是当前的key
if (key.equals(mArray[index<<1])) {
return index;
}
// 往后查找,找到是否是equals
int end;
for (end = index + 1; end < N && mHashes[end] == hash; end++) {
if (key.equals(mArray[end << 1])) return end;
}
// 往前查找,使用equals
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0 && mHashes[i] == hash; i--) {
if (key.equals(mArray[i << 1])) return i;
}
return ~end;
}
从上面的逻辑我们可以看到,mHashes维护的是一个有序的hashcode的数组,同时,array的是两两对应的,一个key,一个value,而key的hashcode和mHashes维护的index是2倍的关系。
如果二分法找到了hash位置,但是并不是equals的。那么就说明我们遇到了hash碰撞了,那么接着可以看一下对应的操作,于是就继续往后或者往前查找,采用key的equals的方式来查找key。那么我们就可以断定——mhashes中其实是存在着重复的hash值,而marray里面的key也是按hashcode的值排列,但是也会考虑equals的情况。
那么总结一下就是:ArrayMap遇到hash碰撞的时候,在mHashes中重复碰撞的值,而在mArray中保存对应的key,和value来保证数据的完整。
ArrayMap的内存优化原理
首先需要从put方法说起来:
public V put(K key, V value) {
final int osize = mSize;
final int hash;
...//查找index的上面已经说过
index = ~index;
if (osize >= mHashes.length) { // 如果需要扩容
final int n = osize >= (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (osize+(osize>>1))
: (osize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE*2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n); // 申请内存
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS && osize != mSize) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + osize + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, osize); // 释放内存
}
if (index < osize) { //进行copy操作
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: move " + index + "-" + (osize-index)
+ " to " + (index+1));
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index, mHashes, index + 1, osize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, index << 1, mArray, (index + 1) << 1, (mSize - index) << 1);
}
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS) {
if (osize != mSize || index >= mHashes.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
mHashes[index] = hash;
mArray[index<<1] = key;
mArray[(index<<1)+1] = value;
mSize++;
return null;
}
其实我们从put的扩容中就可以推出对应的复用机制。我们现在模拟一个情况:
ArrayMap map = new ArrayMap<>(4);
map.put(*,*);
map.put(*,*);
map.put(*,*);
map.put(*,*);
// put进第五个数需要扩容
map.put(*,*);
首先创建的时候会使用allocArrays
private void allocArrays(final int size) {
if (mHashes == EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("ArrayMap is immutable");
}
if (size == (BASE_SIZE*2)) {
synchronized (ArrayMap.class) {
if (mTwiceBaseCache != null) {
final Object[] array = mTwiceBaseCache;
mTwiceBaseCache = (Object[])array[0];
mHashes = (int[])array[1];
mArray = array;
array[0] = array[1] = null;
mTwiceBaseCacheSize--;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Retrieving 2x cache " + mHashes
+ " now have " + mTwiceBaseCacheSize + " entries");
return;
}
}
} else if (size == BASE_SIZE) {
synchronized (ArrayMap.class) {
if (mBaseCache != null) {
final Object[] array = mBaseCache;
mBaseCache = (Object[])array[0];
mHashes = (int[])array[1];
mArray = array;
array[0] = array[1] = null;
mBaseCacheSize--;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Retrieving 1x cache " + mHashes
+ " now have " + mBaseCacheSize + " entries");
return;
}
}
}
mHashes = new int[size];
mArray = new Object[size<<1];
}
但是其实此时mbasecache和mTwiceBaseCache都是null,所以并不会初始化,此时情况就是
//mHashes的长度是4
//mArray的长度是8
//mBaseCache 和 mTwiceBaseCache都是null
那put到第四个都可以接受,但是put到第五个的时候。就需要进行扩容处理。让我们看一下扩容处理。
//查看上面allocArray的代码,可以看到由于mBaseCache 和 mTwiceBaseCache都是null,只是将mHashes和mArray进行了扩容。也就是变成了8和16.而且将旧数据保存在ohashes和oarray中。然后将旧数组的内容copy在新数组中。
if (osize >= mHashes.length) { // 如果需要扩容
final int n = osize >= (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (osize+(osize>>1))
: (osize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE*2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes; // 保存旧数据
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n); // 申请内存 —— 上面说到的,就是将两个数组进行扩容
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS && osize != mSize) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
if (mHashes.length > 0) { // 此处将原数组copy到新数组中
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + osize + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, osize); // 释放内存
}
然后就来到了最关键的地方,也就是freeArrays
private static void freeArrays(final int[] hashes, final Object[] array, final int size) {
if (hashes.length == (BASE_SIZE*2)) {
synchronized (ArrayMap.class) {
if (mTwiceBaseCacheSize < CACHE_SIZE) {
array[0] = mTwiceBaseCache;
array[1] = hashes;
for (int i=(size<<1)-1; i>=2; i--) {
array[i] = null;
}
mTwiceBaseCache = array;
mTwiceBaseCacheSize++;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Storing 2x cache " + array
+ " now have " + mTwiceBaseCacheSize + " entries");
}
}
} else if (hashes.length == BASE_SIZE) { // ohash的length是4,所以走这个通路
synchronized (ArrayMap.class) {
if (mBaseCacheSize < CACHE_SIZE) {
array[0] = mBaseCache; // 为null
array[1] = hashes; // 保存hashs
for (int i=(size<<1)-1; i>=2; i--) {
array[i] = null; // 将后面都置成null
}
mBaseCache = array; // 将这个数组赋值给mBaseCache
mBaseCacheSize++;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Storing 1x cache " + array
+ " now have " + mBaseCacheSize + " entries");
}
}
}
}
这里就可以看到首先将之前的array数组清空,然后array[0]指向了之前的数组,而array[1]则指向了hashes数组。再将这个数组赋值给mBaseCache。
那么就可以总结为:当在需要进行扩容的时候,将原有的hashes和marray,都保存在mbasecache中。相当于将原有数组进行了一个缓存,反推,在下次allocarray的时候,如果是申请的是4个或者8个,那么我们就可以从之前的缓存的数组中取出来,然后进行赋值操作。所以,其实ArrayMap的缓存就是缓存的之前所使用过的数组。但是也只有4和8长度的数组会进行缓存。而并不是缓存之前使用过的对象。