2.事件的读取
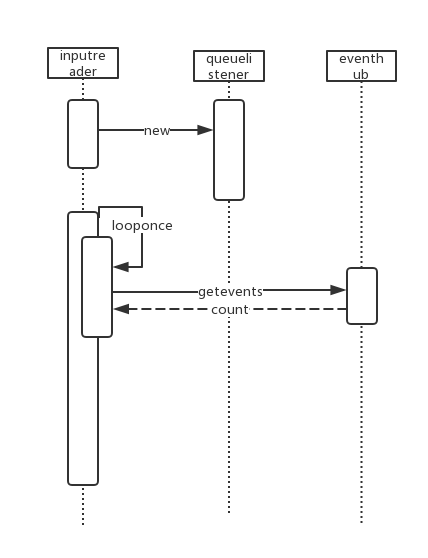
上次我们说到是如何将reader以及dispatcher连接在一起的。那我们现在来看看reader是如何将事件读取出来的。在创建的时候,注意此处的listener就是inputdispatcher哦。
335InputReader::InputReader(const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
336 const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
337 const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) :
338 mContext(this), mEventHub(eventHub), mPolicy(policy),
339 mGlobalMetaState(0), mGeneration(1),
340 mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout(LLONG_MIN), mNextTimeout(LLONG_MAX),
341 mConfigurationChangesToRefresh(0) {
342 mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener);//创建一个queuelistener
然后是在start的时候:
1033bool InputReaderThread::threadLoop() {
1034 mReader->loopOnce();
1035 return true;
1036}
358void InputReader::loopOnce() {
...
380 size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);
381
...
386 if (count) {
387 processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
388 }
...
419 mQueuedListener->flush();
420}
所以现在就是inputreader持有一个queuelistener,而这个queuelistener持有了inputdispatcher
有两个关键的方法,一个是从eventhub中取出对应的事件,另外一个是将事件flush出去。
这就是一次eventhub事件的获取了。
先看是如何取出事件的吧。
741size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
//可以看到一个无限循环
751 for (;;) {
//首先进行了device的初始化
752 nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
753
754 // Reopen input devices if needed.
755 if (mNeedToReopenDevices) {
756 mNeedToReopenDevices = false;
757
758 ALOGI("Reopening all input devices due to a configuration change.");
759
760 closeAllDevicesLocked();
761 mNeedToScanDevices = true;
762 break; // return to the caller before we actually rescan
763 }
764
765 // Report any devices that had last been added/removed.
766 while (mClosingDevices) {
767 Device* device = mClosingDevices;
768 ALOGV("Reporting device closed: id=%d, name=%s\n",
769 device->id, device->path.string());
770 mClosingDevices = device->next;
771 event->when = now;
772 event->deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD_ID : device->id;
773 event->type = DEVICE_REMOVED;
774 event += 1;
775 delete device;
776 mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
777 if (--capacity == 0) {
778 break;
779 }
780 }
781
782 if (mNeedToScanDevices) {
783 mNeedToScanDevices = false;
784 scanDevicesLocked(); //扫描/dev/input/目录来生成device数据
785 mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
786 }
787
788 while (mOpeningDevices != NULL) {
789 Device* device = mOpeningDevices;
790 ALOGV("Reporting device opened: id=%d, name=%s\n",
791 device->id, device->path.string());
792 mOpeningDevices = device->next;
793 event->when = now;
794 event->deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;
795 event->type = DEVICE_ADDED;
796 event += 1;
797 mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
798 if (--capacity == 0) {
799 break;
800 }
801 }
802
803 if (mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan) {
804 mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = false;
805 event->when = now;
806 event->type = FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN;
807 event += 1;
808 if (--capacity == 0) {
809 break;
810 }
811 }
首先获取到当前所有的可以有input事件的device,下面就需要进行第二步了。
1011
1012 int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
1013
就是在epoll上wait,等待消息。
这个时候就来到了事件的处理了
814 bool deviceChanged = false;
815 while (mPendingEventIndex < mPendingEventCount) {
816 const struct epoll_event& eventItem = mPendingEventItems[mPendingEventIndex++];
817 if (eventItem.data.u32 == EPOLL_ID_INOTIFY) {
818 if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
819 mPendingINotify = true;
820 } else {
821 ALOGW("Received unexpected epoll event 0x%08x for INotify.", eventItem.events);
822 }
823 continue;
824 }
825
826 if (eventItem.data.u32 == EPOLL_ID_WAKE) {
827 if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
828 ALOGV("awoken after wake()");
829 awoken = true;
830 char buffer[16];
831 ssize_t nRead;
832 do {
833 nRead = read(mWakeReadPipeFd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
834 } while ((nRead == -1 && errno == EINTR) || nRead == sizeof(buffer));
835 } else {
836 ALOGW("Received unexpected epoll event 0x%08x for wake read pipe.",
837 eventItem.events);
838 }
839 continue;
840 }
841
842 ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(eventItem.data.u32);
843 if (deviceIndex < 0) {
844 ALOGW("Received unexpected epoll event 0x%08x for unknown device id %d.",
845 eventItem.events, eventItem.data.u32);
846 continue;
847 }
848
849 Device* device = mDevices.valueAt(deviceIndex);
850 if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
851 int32_t readSize = read(device->fd, readBuffer,
852 sizeof(struct input_event) * capacity);
853 if (readSize == 0 || (readSize < 0 && errno == ENODEV)) {
854 // Device was removed before INotify noticed.
855 ALOGW("could not get event, removed? (fd: %d size: %" PRId32
856 " bufferSize: %zu capacity: %zu errno: %d)\n",
857 device->fd, readSize, bufferSize, capacity, errno);
858 deviceChanged = true;
859 closeDeviceLocked(device);
860 } else if (readSize < 0) {
861 if (errno != EAGAIN && errno != EINTR) {
862 ALOGW("could not get event (errno=%d)", errno);
863 }
864 } else if ((readSize % sizeof(struct input_event)) != 0) {
865 ALOGE("could not get event (wrong size: %d)", readSize);
866 } else {
867 int32_t deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;
868
869 size_t count = size_t(readSize) / sizeof(struct input_event);
870 for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
871 struct input_event& iev = readBuffer[i];
872 ALOGV("%s got: time=%d.%06d, type=%d, code=%d, value=%d",
873 device->path.string(),
874 (int) iev.time.tv_sec, (int) iev.time.tv_usec,
875 iev.type, iev.code, iev.value);
876
877 // Some input devices may have a better concept of the time
878 // when an input event was actually generated than the kernel
879 // which simply timestamps all events on entry to evdev.
880 // This is a custom Android extension of the input protocol
881 // mainly intended for use with uinput based device drivers.
882 if (iev.type == EV_MSC) {
883 if (iev.code == MSC_ANDROID_TIME_SEC) {
884 device->timestampOverrideSec = iev.value;
885 continue;
886 } else if (iev.code == MSC_ANDROID_TIME_USEC) {
887 device->timestampOverrideUsec = iev.value;
888 continue;
889 }
890 }
891 if (device->timestampOverrideSec || device->timestampOverrideUsec) {
892 iev.time.tv_sec = device->timestampOverrideSec;
893 iev.time.tv_usec = device->timestampOverrideUsec;
894 if (iev.type == EV_SYN && iev.code == SYN_REPORT) {
895 device->timestampOverrideSec = 0;
896 device->timestampOverrideUsec = 0;
897 }
898 ALOGV("applied override time %d.%06d",
899 int(iev.time.tv_sec), int(iev.time.tv_usec));
900 }
901
902 // Use the time specified in the event instead of the current time
903 // so that downstream code can get more accurate estimates of
904 // event dispatch latency from the time the event is enqueued onto
905 // the evdev client buffer.
906 //
907 // The event's timestamp fortuitously uses the same monotonic clock
908 // time base as the rest of Android. The kernel event device driver
909 // (drivers/input/evdev.c) obtains timestamps using ktime_get_ts().
910 // The systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC) function we use everywhere
911 // calls clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC) which is implemented as a
912 // system call that also queries ktime_get_ts().
913 event->when = nsecs_t(iev.time.tv_sec) * 1000000000LL
914 + nsecs_t(iev.time.tv_usec) * 1000LL;
915 ALOGV("event time %" PRId64 ", now %" PRId64, event->when, now);
916
917 // Bug 7291243: Add a guard in case the kernel generates timestamps
918 // that appear to be far into the future because they were generated
919 // using the wrong clock source.
920 //
921 // This can happen because when the input device is initially opened
922 // it has a default clock source of CLOCK_REALTIME. Any input events
923 // enqueued right after the device is opened will have timestamps
924 // generated using CLOCK_REALTIME. We later set the clock source
925 // to CLOCK_MONOTONIC but it is already too late.
926 //
927 // Invalid input event timestamps can result in ANRs, crashes and
928 // and other issues that are hard to track down. We must not let them
929 // propagate through the system.
930 //
931 // Log a warning so that we notice the problem and recover gracefully.
932 if (event->when >= now + 10 * 1000000000LL) {
933 // Double-check. Time may have moved on.
934 nsecs_t time = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
935 if (event->when > time) {
936 ALOGW("An input event from %s has a timestamp that appears to "
937 "have been generated using the wrong clock source "
938 "(expected CLOCK_MONOTONIC): "
939 "event time %" PRId64 ", current time %" PRId64
940 ", call time %" PRId64 ". "
941 "Using current time instead.",
942 device->path.string(), event->when, time, now);
943 event->when = time;
944 } else {
945 ALOGV("Event time is ok but failed the fast path and required "
946 "an extra call to systemTime: "
947 "event time %" PRId64 ", current time %" PRId64
948 ", call time %" PRId64 ".",
949 event->when, time, now);
950 }
951 }
952 event->deviceId = deviceId;
953 event->type = iev.type;
954 event->code = iev.code;
955 event->value = iev.value;
956 event += 1;
957 capacity -= 1;
958 }
959 if (capacity == 0) {
960 // The result buffer is full. Reset the pending event index
961 // so we will try to read the device again on the next iteration.
962 mPendingEventIndex -= 1;
963 break;
964 }
965 }
966 } else if (eventItem.events & EPOLLHUP) {
967 ALOGI("Removing device %s due to epoll hang-up event.",
968 device->identifier.name.string());
969 deviceChanged = true;
970 closeDeviceLocked(device);
971 } else {
972 ALOGW("Received unexpected epoll event 0x%08x for device %s.",
973 eventItem.events, device->identifier.name.string());
974 }
975 }
976
需要注意代码中的逻辑处理其实是在读取前面的,因为for循环的原因,在处理了之后会进行break,所以在最后会
1040 return event - buffer;
此时,那么从eventhub中读取事件就已经完成了。总结一下就是,首先,inputreader调用了getevents,getevents其实分成了三部分,首先是进行device的读取和处理,读取了之后生成对应的device数据结构。第二步看有没有需要处理的时间,如果有那么就处理了返回。第三步就是进行等待,等待对应事件的发生。
UML时序图: